Value-based care has emerged as an alternative and potential replacement for fee-for-service reimbursement based on quality rather than quantity.
March 02, 2022 – Value-based care is a form of reimbursement that ties payments for care delivery to the quality of care provided and rewards providers for both efficiency and effectiveness. This form of reimbursement has emerged as an alternative and potential replacement for fee-for-service reimbursement, which pays providers retrospectively for services delivered based on bill charges or annual fee schedules.
In order to transform how healthcare providers are reimbursed for services rendered, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) has itself introduced an array of value-based care models, such as the Medicare Shared Savings Program, Next Generation ACO Model, and Pioneer Accountable Care Organization (ACO) Model. Private payers have, in turn, adopted similar models of accountable, value-based care.
While the traditional fee-for-service reimbursement model promoted the quantity of services, federal officials have proposed several reimbursement programs that reward healthcare providers for the quality of care that they give to patients. Value-based care seeks to advance the triple aim of providing better care for individuals, improving population health management strategies, and reducing healthcare costs.
In more basic terms, value-based care models center on patient outcomes and how well healthcare providers can improve quality of care based on specific measures, such as reducing hospital readmissions, using certified health IT, and improving preventative care.
The Department of Health & Human Services (HHS) set a goal of converting 30 percent of fee-for-service Medicare payments to value-based payment models by the end of 2016. The agency also expected 50 percent of traditional payments to make the transition by 2018.
Yet, data shows that only 38.2 percent of healthcare dollars flowed through some type of value-based payment model as of 2019.
As the healthcare industry transitions to this new way of delivering care, many healthcare providers are left wondering how value-based care differs from the traditional model, what programs are available, and how successful it has been?
The following sections will examine the basics of value-based care and help readers understand how the model works.
HOW IS VALUE-BASED CARE DIFFERENT FROM FEE-FOR-SERVICE MODELS?
In the traditional fee-for-service reimbursement model, healthcare providers were paid for the number of services they performed. This has incentivized many providers to order more tests and procedures and manage more patients to get paid more.
The costs were determined by what commercial payers would pay in the private market and a percentage of what Medicare would have paid for similar services. Rates for services were also unbundled, meaning each service was paid for separately.
“The goal is straightforward but ambitious: Replace the nation’s reliance on fragmented, fee-for-service care with comprehensive, coordinated care using payment models that hold organizations accountable for cost control and quality gains.”
Under fee-for-service models, cost variations for procedures and tests increased, and the healthcare industry was spending more to treat patients even though patient outcomes were not necessarily improving. The model also challenged provider workflows because physicians saw more patients, and each claim had to be processed in a fragmented network.
The federal government designed value-based care programs to drive down healthcare costs and improve patient outcomes. These reimbursement and care models hinge on advancing quality of care while increasing patient access and accounting for price at the point of care.
“The opportunity exists to transform how healthcare is delivered,” explained a State Health Care Cost Containment Committee report. “The goal is straightforward but ambitious: Replace the nation’s reliance on fragmented, fee-for-service care with comprehensive, coordinated care using payment models that hold organizations accountable for cost control and quality gains.”
Value-based reimbursements are calculated by using numerous quality measures and determining the overall health of populations. Unlike the traditional model, value-based care is driven by data because providers must report to payers on specific metrics and demonstrate improvement. Providers may have to track and report on hospital readmissions, adverse events, population health, patient engagement, and more.
Under the new models, providers are incentivized to use evidence-based medicine, engage patients, upgrade health IT, and use data analytics to get paid for their services. When patients receive more coordinated, appropriate, and effective care, providers are rewarded.
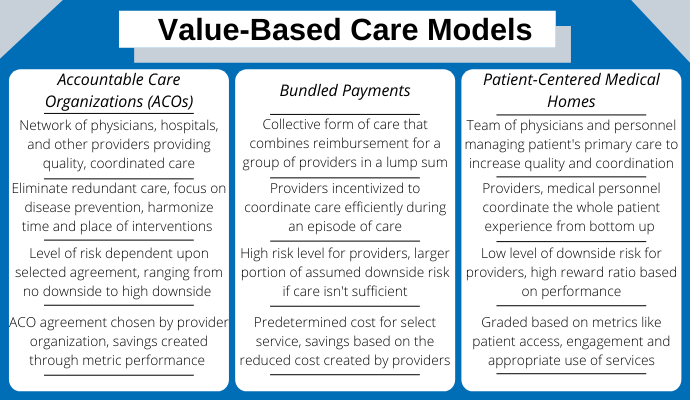
To participate in value-based care, CMS has developed several models for providers, such as the accountable care organization, bundled payments, and patient-centered medical homes.
WHAT VALUE-BASED CARE MODELS ARE AVAILABLE?